Custom Medical Machining & Machined Parts
Soaring above expectations
Our industrial machine shop services include aerospace parts machining and machined aerospace products. At Cox Manufacturing, we have a two-pronged approach to the stratospheric material and process requirements of the aerospace industry. We rise to the challenge of crafting high precision components designed for modern flight vehicles, while consistently maintaining the rigorous standard of on-time delivery and reliable quality we’ve upheld for half a century.

Medical Machining Services
Professionals in the Medical Industry know they can count on our full complement of machining capabilities:
- The exceptional precision of CNC Swiss machining
- Multi spindle cam automatics
- CNC turning and milling up to 12-axis machine centers
- An Esprit CAD/CAM system to precisely produce the most elaborate geometries (complete equipment list)
Certifications & Standards
Our mastery of high performance materials such as titanium, stainless, exotic alloys and high temperature plastics makes us the rising star in aerospace component manufacturing. Our ISO 9001:2015 quality system, compliance with ITAR controls, and extensive knowledge of DFARS materials source requirements makes Cox fully compatible with aerospace industry expectations.
In an industry where a mission’s success hinges on the quality of each individual component, Cox takes pride in its track record as a trusted supplier to the innovators in aerospace design.
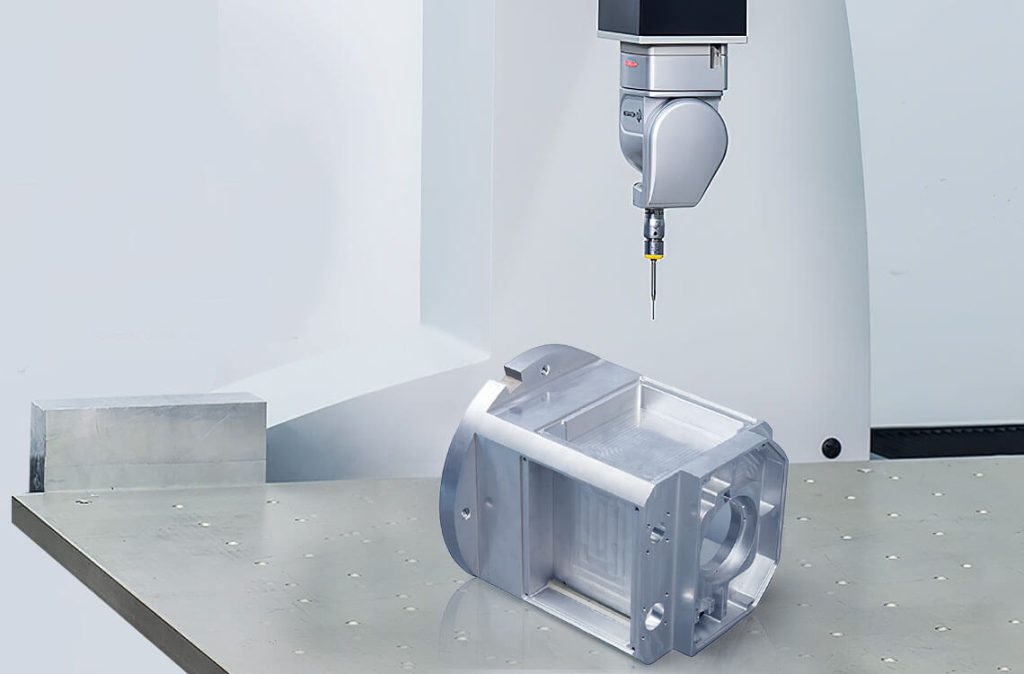
Safe And Machining Capacity
With strong production capacity, more than 100 CNC machining capabilities, up to 500 professional CNC engineers, convenient transportation can quickly deliver your goods.

Professional Quick Quote
Professional quotation engineers can give price and delivery date within one working day, with 20% discount for the first order. Accept drawings of various types of documents, including STEP, Mesh, Parasolid, and ACIS files.

Quality Assurance
The company has passed EN9100&ISO9001 Certification,Delivery in as fast as 5 days /100% Inspection /FullProeess Measurement Report /3D Scanning Digital AnalogComparison /Pree Return and Exchange of Defective Products.
Rapid Manufacturing on Demand
Our reliable rapid prototyping services have served many customers representing different phases of the aerospace industry. Consequently, we have adjusted our systems to ensure that any order, regardless of volume, is produced and delivered at the right time for each customer. Our production systems can produce parts in small, batch, or large-scale quantities, and the most important aspect is that our quality standards remain high. The product design stage at our company is reduced since we only use the right tools that can quickly capture all the relevant product details. We can quickly create aerospace part prototypes and show them to customers who may then decide if certain changes must be made to the original design.
Medical Machining Materials
From prototyping to full production runs. Our wide range of CNC lathes and turning centers will allow you to produce highly accurate, high quality parts to meet even your most stringent requirements.
| AEROSPACE MACHINING MATERIALS | ||
| Alloys | Stainless Steel | |
| METALS | Aluminum | Precision Steel |
| Brass | Titanium | |
| Copper | Special Alloys | |
| PVC | UHMW | |
| PLASTICS | Nylon | Ultem |
| Delrin | PEEK | |
| PTFE | Acetal |
Top Medical Applications

The division of four processes in CNC machining of medical parts
The design and development of medical devices is the key stage of its success, and in the production of medical devices, cnc processing is particularly important. CNC machining offers the advantages of a high degree of customization, tight tolerances, good surface finish and certified material selection. When machining with cnc, parts are usually milled with 3 to 5 axes or turned with a live tool CNC lathe. Manufactured items include various surgical instruments used in medical procedures, such as trocars (skin passers), bone drills, and saws.
Four requirements for medical parts processing
For parts with many and complex CNC machining surfaces, the sequence of CNC machining, heat treatment and auxiliary processes should be reasonably arranged, and the problem of connection between processes should be solved. Before clamping the raw material, measure whether the size of the blank meets the requirements of the drawing, and carefully check whether its placement is consistent with the programming instructions. In CNC machining, self-check should be carried out in time after the roughing process is completed, so as to adjust the error data in time. The content of self-inspection mainly includes the position and size of the processing part:
(1) Whether the mechanical parts are loose during processing;
(2) Whether the processing technology of medical parts is correct to touch the starting point;
(3) Whether the size of the CNC machining part to the reference edge (reference point) conforms to the drawing requirements;
(4) The location and size of medical parts. After checking the position and size, measure the roughed shape ruler (except arcs).
Tolerances
| Limits for nominal size | Plastics (ISO 2768- m) | Metals (ISO 2768- f) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5mm* to 3mm | ±0.1mm | ±0.05mm |
| Over 3mm to 6mm | ±0.1mm | ±0.05mm |
| Over 6mm to 30mm | ±0.2mm | ±0.1mm |
| Over 30mm to 120mm | ±0.3mm | ±0.15mm |
| Over 120mm to 400mm | ±0.5mm | ±0.2mm |
| Over 2000mm to 4000mm | ±2mm |




